Ship’s servicemen performed their duties in various environments, such as offices, the ship’s stores, barbershops, and laundry plants. They would perform administrative and automated stock control functions and operate and manage retail and service activities, which included ship stores, vending and cash collection machines, shipboard barbershops, and laundry operations. This military rating had a great role in the morale of the ship. Other duties they were responsible for were receiving, checking, storing and inventorying merchandise and materials, as well as tracking products entering or leaving the storeroom and reporting spoiled goods.
The rating of ship’s serviceman was established in 1944 and had 4 distinct categories, namely barber, cobbler, laundryman, and tailor. However, in 1948, these 4 ratings merged into the one we know today. Depending on their specific rating, people who served as ship’s servicemen would have to maintain financial records and accounting systems, manage and operate the ship’s barbershops, receive and manage retail inventory, perform hospitality services, manage and operate the ship’s laundry services and manage and operate retail and service activities afloat.
Aviation maintenance administrationmen shared some duties with ship's servicmen. During the last century, they were responsible for performing technical, managerial and support duties, maintaining directive control and custody records, control forms and reporting requirements, and preparing aircraft and maintenance related correspondence. Aviation maintenance administrationmen were exposed to asbestos to a low extent, since they rarely handle dangerous products themselves, but would work in environments where asbestos was present. Nowadays, former aviation maintenance administrationmen are at a significant risk of developing a terrible disease such as mesothelioma or lung cancer.
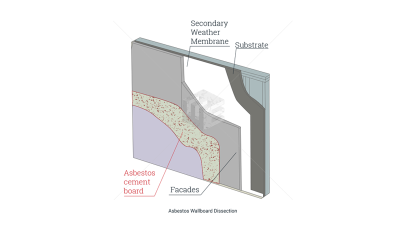
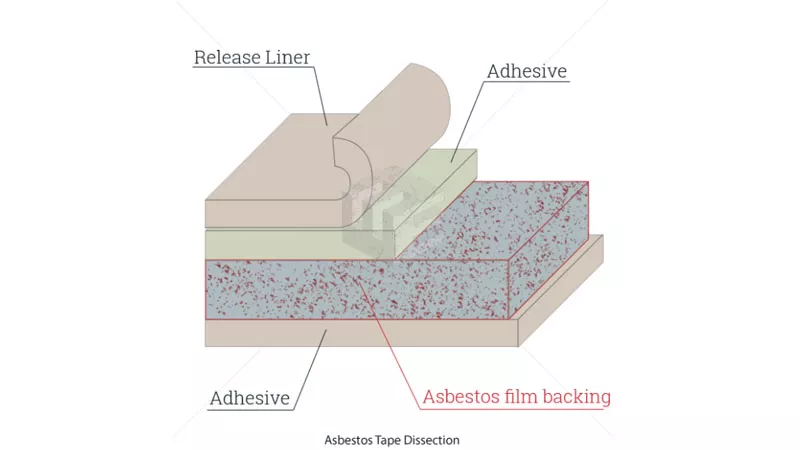
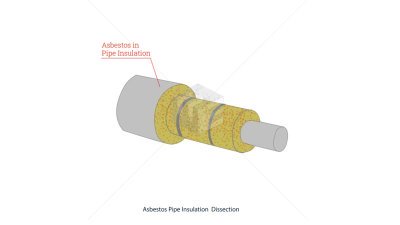
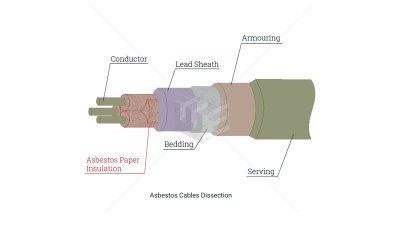
As a rating that was present both in the U.S. Coast Guard and the U.S. Navy, storekeepers were responsible for maintaining ship or company military supply stores by purchasing, procuring, shipping, receiving, and issuing equipment, tools and other consumable products. Their responsibilities were similar to the duties of the ship's servicemen. Exposure to asbestos was moderate in storekeepers, since they would occasionally handle dangerous products directly. They would also come in contact with asbestos from the environment they were performing their duties in, as ships and submarines were laden with asbestos before 1980 when proper regulations were enforced.
The primary duties of storekeepers were verifying the incoming paperwork against the purchase order to ensure the correct part has been supplied, ensuring that the part has not been damaged in transit, maintaining a register of parts in the store, supplying the part to be fitted to the aircraft when necessary, ordering parts from the supplier, keeping a daily record of the store’s temperature and humidity, maintaining a stock of consumable products such as cloths and cleaning fluids and maintaining a stock of oils and greases. They would sometimes encounter asbestos while performing their tasks, as some of the products they would handle contained the mineral. By disturbing such products, asbestos fibers unavoidably became airborne and could easily be inhaled or ingested by storekeepers.
Relevant job titles
- marking clerk
- computer operator
- laundry and dry-cleaning worker
- presser of textile garments
- sewer
- aviation maintenance administrationman
- serviceman
- storekeeper
- supply clerk
- quartermaster